Can You Switch Antibiotics Mid Course
Can You Switch Antibiotics Mid Course - In this blog post, we will explore the potential risks and considerations of switching. It is time to reconsider the widespread advice that people should always complete an entire course of antibiotics, experts in the bmj say. He still believes it is sinus related and said i should switch to amoxicillin. You only have a few more days left, anyways. Note it is important to always finish your antibiotic even if you feel better, as the infection may come back. So, switching would not necessarily cause antibiotic resistant. The reason you should finish the entire course is because a partial course will kill off the weaker bacteria and leave the stronger, possibly resistant, bacteria to grow. For what purpose are you using an antibiotic? You'll want to finish taking your current antibiotics. There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. Switching antibiotics mid course a member asked: A practical intervention resulting in reduce d. Doctors often recommend waiting at least 48 hours after stopping an antibiotic before starting a new one. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help mitigate these risks. If your infection was resistant to previous antibiotic you can. You do not have to wait. In this blog post, we will explore the potential risks and considerations of switching. He still believes it is sinus related and said i should switch to amoxicillin. The reason you should finish the entire course is because a partial course will kill off the weaker bacteria and leave the stronger, possibly resistant, bacteria to grow. This timeframe allows for any lingering effects of the initial medication to dissipate. If you have only completed part of the course of the first antibiotic, you do not need. Sometimes we use a combination of antibiotics. Is it safe to switch. So just as long as the infection is resolved, then you’ll be. Ive had multiple utis with flank pain that subsides. For what purpose are you using an antibiotic? He still believes it is sinus related and said i should switch to amoxicillin. You'll want to finish taking your current antibiotics. I am now wondering if i could switch to amoxicillin for the next 6 days to finish my 10 day course of antibiotics since i feel like it was way. There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. Make sure it is prescribed. You only have a few more days left, anyways. Is it safe to switch. Switching antibiotics mid course a member asked: If you have only completed part of the course of the first antibiotic, you do not need. If your infection was resistant to previous antibiotic you can. He mentioned doing a cbct but wants to wait and see if the antibiotics work. So just as long as the infection is resolved, then you’ll be. Note it is important to always. For what purpose are you using an antibiotic? There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. You'll want to finish taking your current antibiotics. There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. Consulting with. Switching antibiotics mid course a member asked: In this blog post, we will explore the potential risks and considerations of switching. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help mitigate these risks. A practical intervention resulting in reduce d. However, there may be situations where switching antibiotics in the middle of a course becomes necessary. Yes, when changing antibiotics, it is fine to simply stop the first antibiotic and start the second antibiotic. Why do you want to change it? You do not have to wait. What happens if you're given an antibiotic for a respiratory infection but because of side effects need it changed after 2 days? Continuing an antibiotic that is not effective. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help mitigate these risks. Make sure it is prescribed. You do not have to wait. It is a widely accepted fact that stopping a course of antibiotics mid way can cause the pathogens to get immunity from the effects of the drug, causing them to become more. However, there may be situations where switching. Why do you want to change it? You do not have to wait. Is it safe to switch. In this blog post, we will explore the potential risks and considerations of switching. Make sure it is prescribed. What happens if you're given an antibiotic for a respiratory infection but because of side effects need it changed after 2 days? Consulting with a healthcare professional. A practical intervention resulting in reduce d. Sometimes we use a combination of antibiotics. You only have a few more days left, anyways. Note it is important to always finish your antibiotic even if you feel better, as the infection may come back. However, there may be situations where switching antibiotics in the middle of a course becomes necessary. There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. So, switching would not necessarily cause antibiotic resistant. This timeframe allows for any lingering effects of the initial medication to dissipate. Doctors often recommend waiting at least 48 hours after stopping an antibiotic before starting a new one. It is a widely accepted fact that stopping a course of antibiotics mid way can cause the pathogens to get immunity from the effects of the drug, causing them to become more. The reason you should finish the entire course is because a partial course will kill off the weaker bacteria and leave the stronger, possibly resistant, bacteria to grow. Yes, when changing antibiotics, it is fine to simply stop the first antibiotic and start the second antibiotic. There can be risks associated with switching antibiotics midcourse, such as potential for antibiotic resistance and incomplete treatment of the infection. It is time to reconsider the widespread advice that people should always complete an entire course of antibiotics, experts in the bmj say.PPT Bone and joint infections PowerPoint Presentation, free download
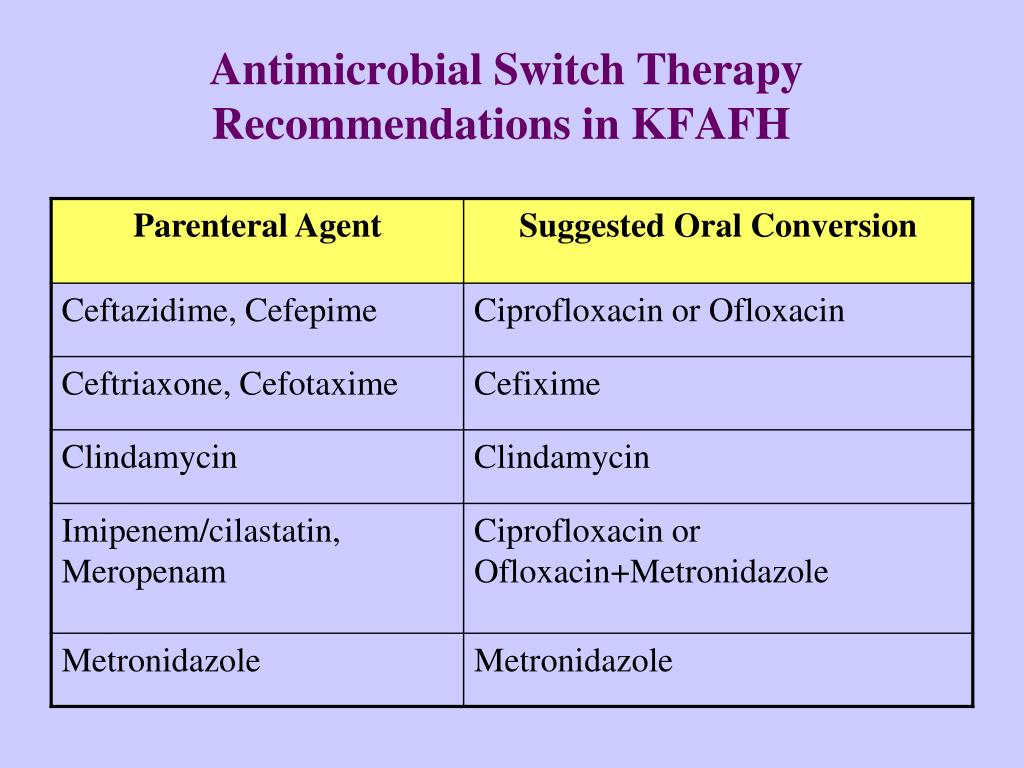
PPT IntravenoustoOral Antibiotic Switch Therapy PowerPoint
PPT IntravenoustoOral Antibiotic Switch Therapy PowerPoint
Change in Antibiotic during infection with the reasons for switching of
Can you switch antibiotics midcourse
Antibiotic for hydronephrosis
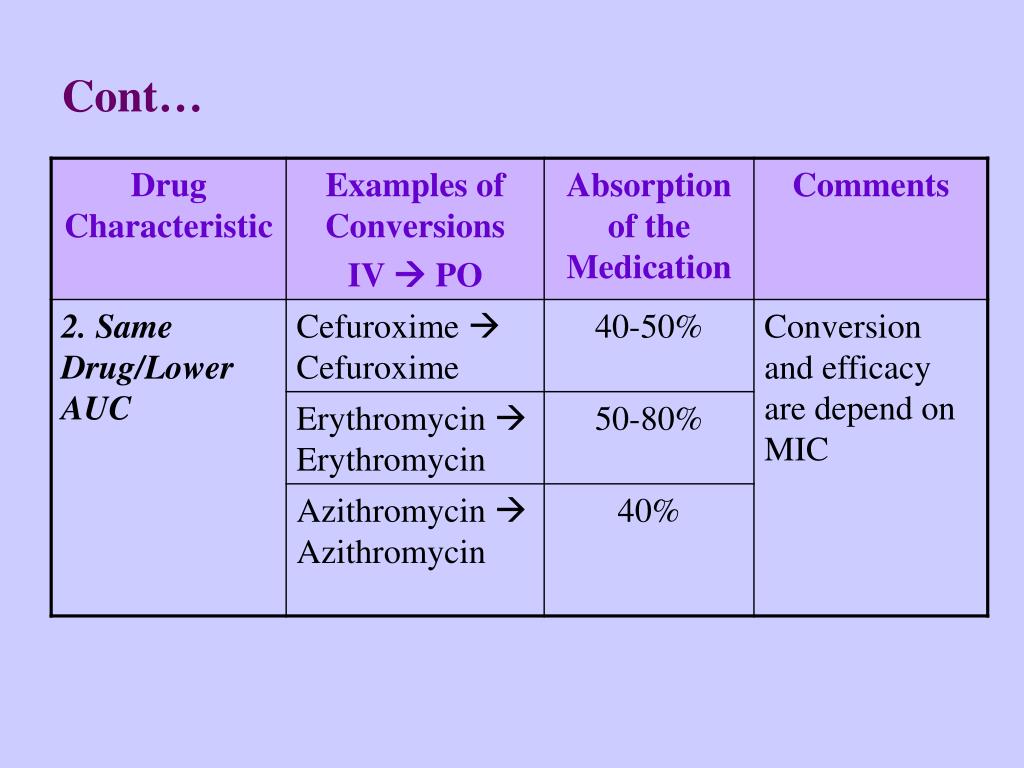
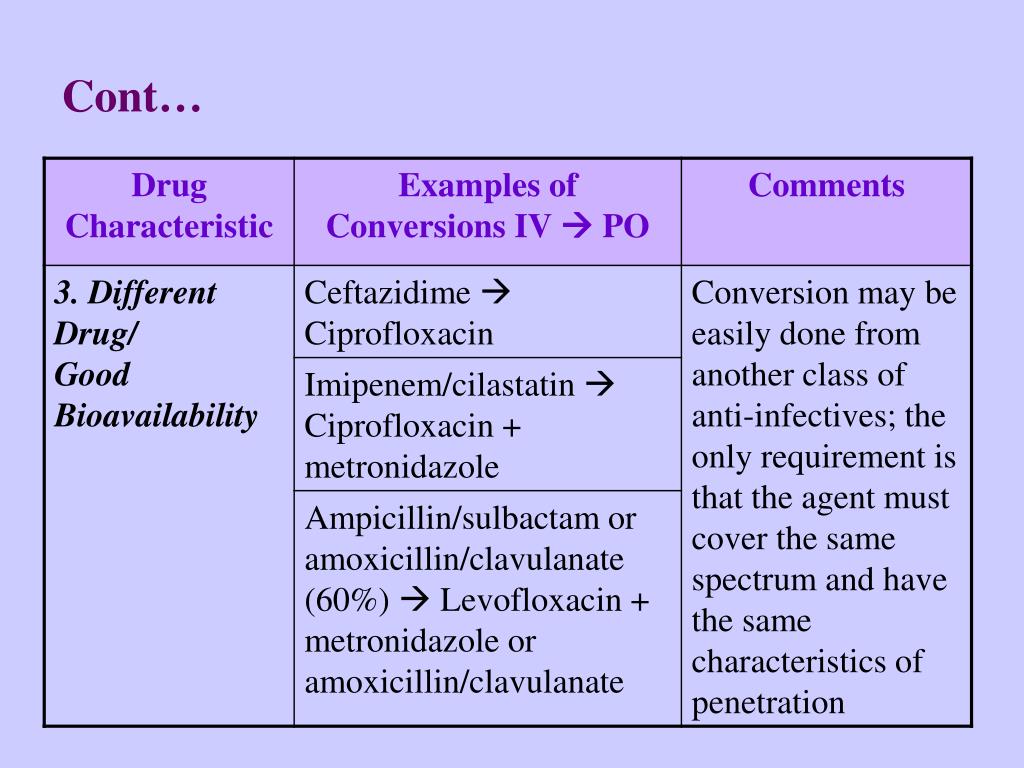
PPT IntravenoustoOral Antibiotic Switch Therapy PowerPoint
PPT IntravenoustoOral Antibiotic Switch Therapy PowerPoint
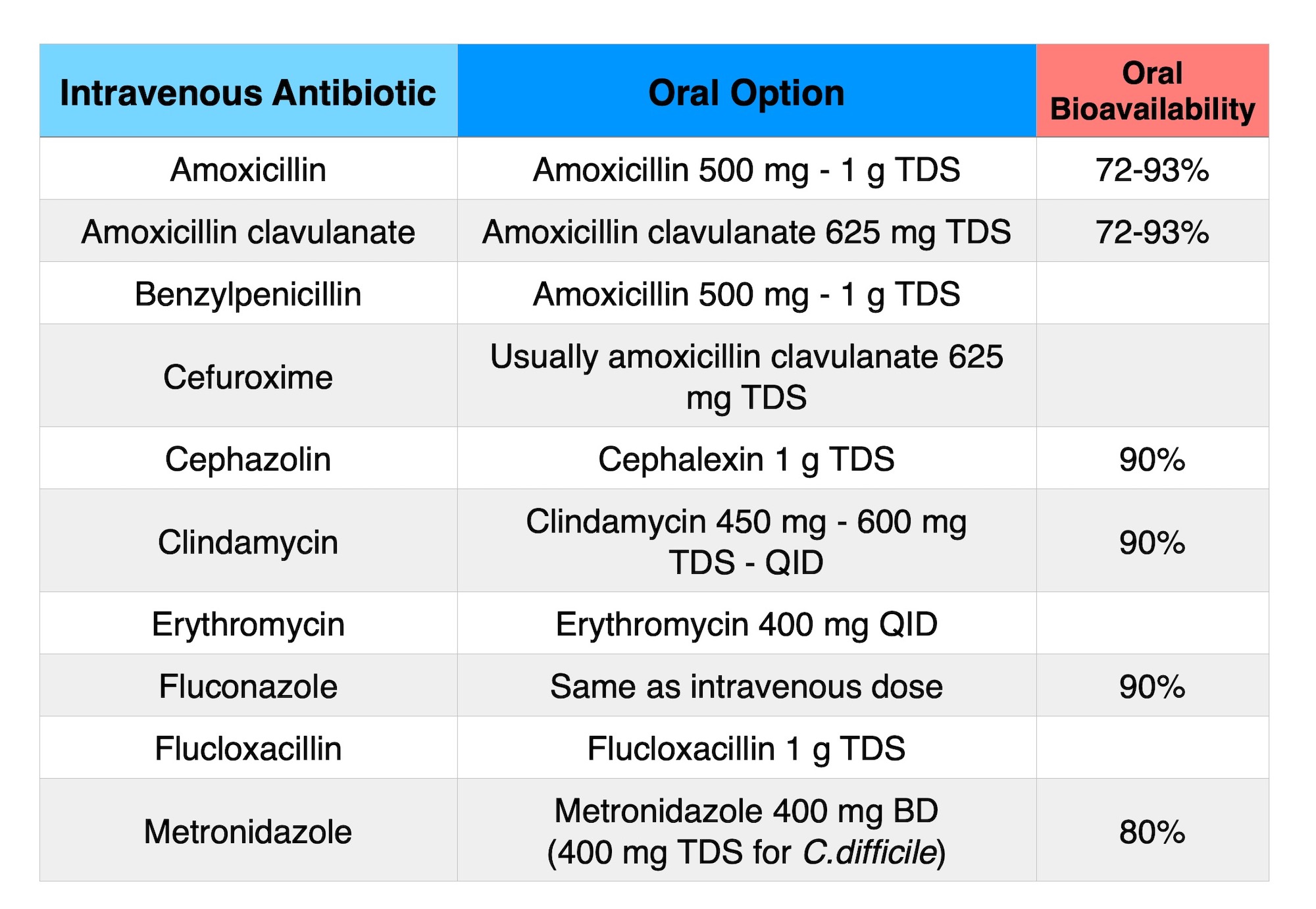
Appendix 8 Intravenous to oral antibiotic conversion
If You Have Only Completed Part Of The Course Of The First Antibiotic, You Do Not Need.
Switching Antibiotics Mid Course A Member Asked:
Why Do You Want To Change It?
So Just As Long As The Infection Is Resolved, Then You’ll Be.
Related Post: